After the success of Chandrayan-3, ISRO launched Aditya L1 mission today. Know the details about this mission and celebrate the missions of ISRO.

The celestial bodies that dance through our universe, including our very own Sun, continue to mystify and captivate humanity’s curiosity. As we venture further into the realms of space exploration, a remarkable mission emerges from the heart of India’s space endeavors – the Aditya L1. This groundbreaking Indian mission, set to become the first space-based initiative to study the Sun, is poised to unlock the secrets of our nearest star.
The Halo Orbit Around Lagrange Point 1 (L1)
Aditya L1, named after the Sun God ‘Aditya’ in Indian mythology, will be strategically placed in a halo orbit around Lagrange Point 1 (L1) of the Sun-Earth system, approximately 1.5 million kilometers from Earth. This unique vantage point offers an unparalleled advantage – a continuous view of the Sun without the interruption of occultations or eclipses. This means Aditya L1 will have an uninterrupted view of the Sun, providing real-time observations of solar activities and their impact on space weather.
The Instruments on Board
Equipped with seven state-of-the-art payloads, Aditya L1 is ready to explore the Sun’s enigmatic layers: the photosphere, chromosphere, and the outermost corona. These payloads employ a diverse range of electromagnetic, particle, and magnetic field detectors to capture the Sun’s various facets. Four of these instruments will directly observe the Sun, while the remaining three will conduct in-situ studies of particles and fields at L1, contributing crucial scientific insights into the dynamics of solar phenomena in the interplanetary medium.
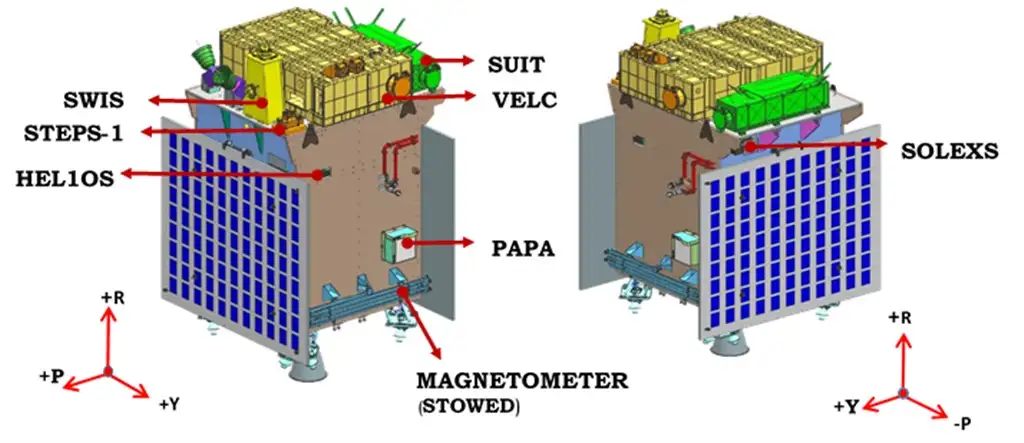
Unveiling the Mysteries of the Sun
The Aditya L1 payloads are expected to provide invaluable insights into several critical areas of solar physics and space weather:
1. Solar Upper Atmospheric Dynamics: One of the primary objectives is to study the dynamics of the Sun’s upper atmosphere, including the chromosphere and corona. This will help scientists better understand the processes responsible for heating these regions and the initiation of phenomena like coronal mass ejections and solar flares.
2. Partially Ionized Plasma: Aditya L1 aims to delve into the physics of partially ionized plasma within the Sun’s atmosphere, shedding light on the complex interactions that occur in this environment.
3. In-situ Particle and Plasma Environment: The mission will provide vital data on the dynamics of particles emanating from the Sun, aiding in the study of particle behavior in the space surrounding our star.
4. Solar Corona and its Heating Mechanism: By examining the solar corona and its heating mechanisms, Aditya L1 aims to tackle one of the most intriguing questions in solar physics – why is the Sun’s outermost layer hotter than its surface?
5. Diagnostics of Coronal Plasma: Temperature, velocity, and density measurements of the coronal plasma will offer deeper insights into the Sun’s behavior.
6. Development and Dynamics of Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs): Understanding the origins and dynamics of CMEs is crucial for space weather forecasting and the protection of satellite and terrestrial communication systems.
7. Magnetic Field Measurements: Aditya L1 will map the magnetic field topology within the solar corona, shedding light on the magnetic forces shaping our star.
8. Drivers for Space Weather: The mission will also investigate the origins, composition, and dynamics of the solar wind, providing essential information for space weather forecasting.
Conclusion
The Aditya L1 mission represents a significant leap forward in India’s space exploration capabilities, and it holds the promise of unraveling some of the Sun’s deepest mysteries. By placing a spacecraft in a halo orbit around L1, scientists will have an unobstructed view of our star, enabling groundbreaking research in solar physics and space weather forecasting. As Aditya L1 embarks on its mission to study the Sun, it carries with it the hopes and expectations of a world eager to comprehend the celestial body that sustains life on Earth and influences the vast expanse of space that surrounds us.
Keep visiting The Ganga Times for such beautiful articles. Follow us on Google News, Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and Koo for regular updates.
